Jalapravesha Parva is the seventy-fifth Upa parva included in the ninth Maha parva named as Shalya parva. Vaishampayana continued narration to Janamejaya in reply to his queries as follows.
What is Hridapravesha?
Hridapravesha means the same as Jalapravesha. It means hiding under water.
What was advised by Krishna to Yudhishtira regaring Shalya?
तवैव हि जयो नूनं हते मद्रेश्वरे युधि ।
तस्मिन् हते हतं सर्वं दार्तराष्ट्र बलं महत् ॥
Krishna advised Yudhishtira, after killing the king of Madra, success would be yours. In the war, if Shalya, the king of Madra is killed, then all great powers of Dritarashtra would be ceased. On the seventeenth day, Yudhishtira killed Shalya.
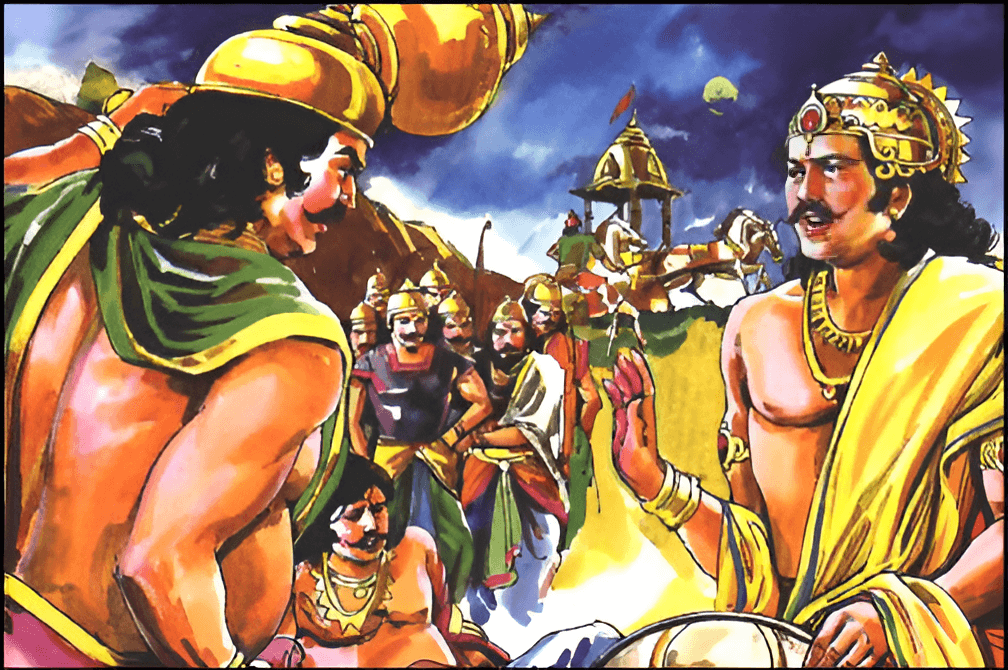
What did Duryodhana and Yudhishtira do after the death of all Kaurava commanders one by one, on the seventeenth day evening?
On the seventeenth day evening, when the Madra king Shalya was killed by Yudhishtira, he was confident about the full success and hence met Krishna with his brothers. Yudhishtira consulted Krishna regarding the next actions.
Krishna told them to take rest for some time at a secret place. Hence they told their charioteers to go to safe places and have rest there at night but not to go to army camps for resting. In the chariot of Yudhishtira, the five brothers had gone to the pig sty near Oghavathy tributary river side. Very secretly, they had rest inside the pig sty after their evening prayers.
Continue reading